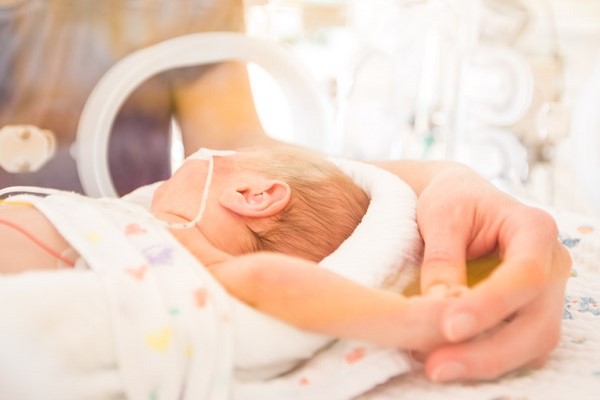
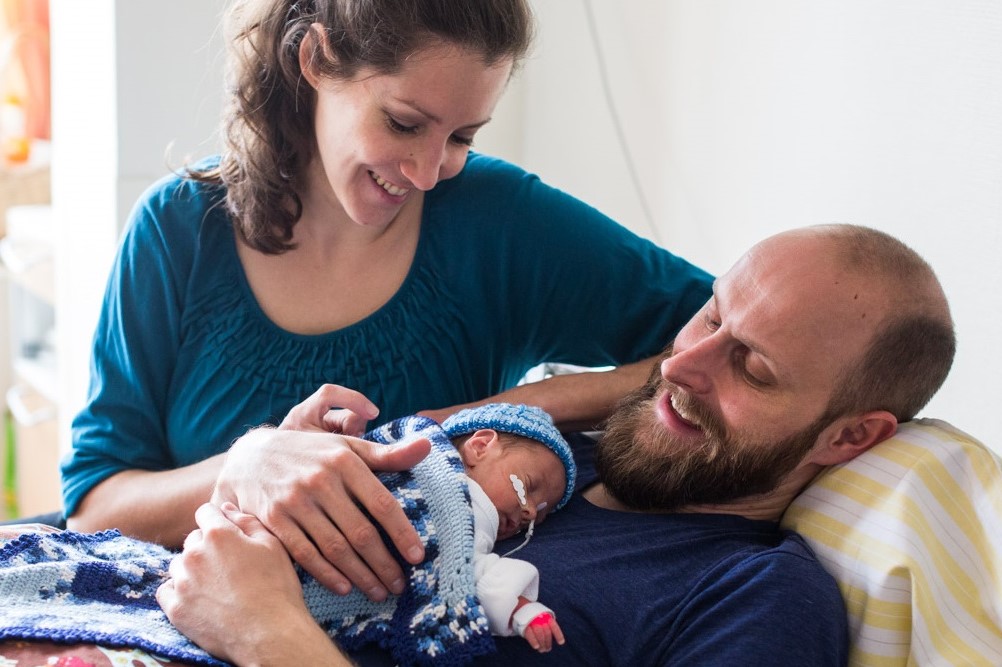
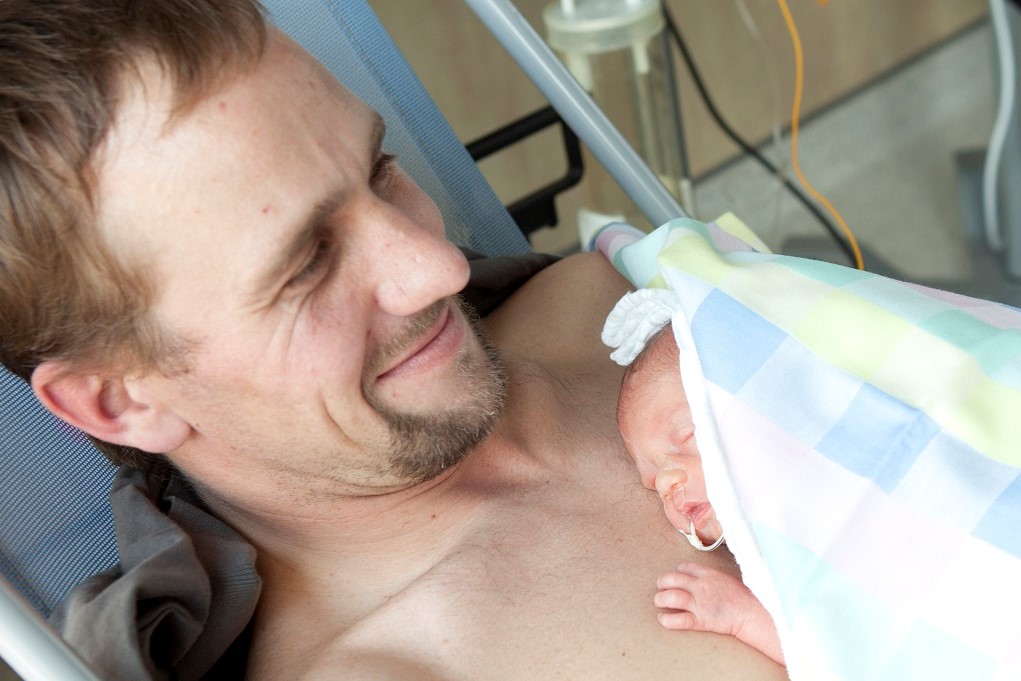
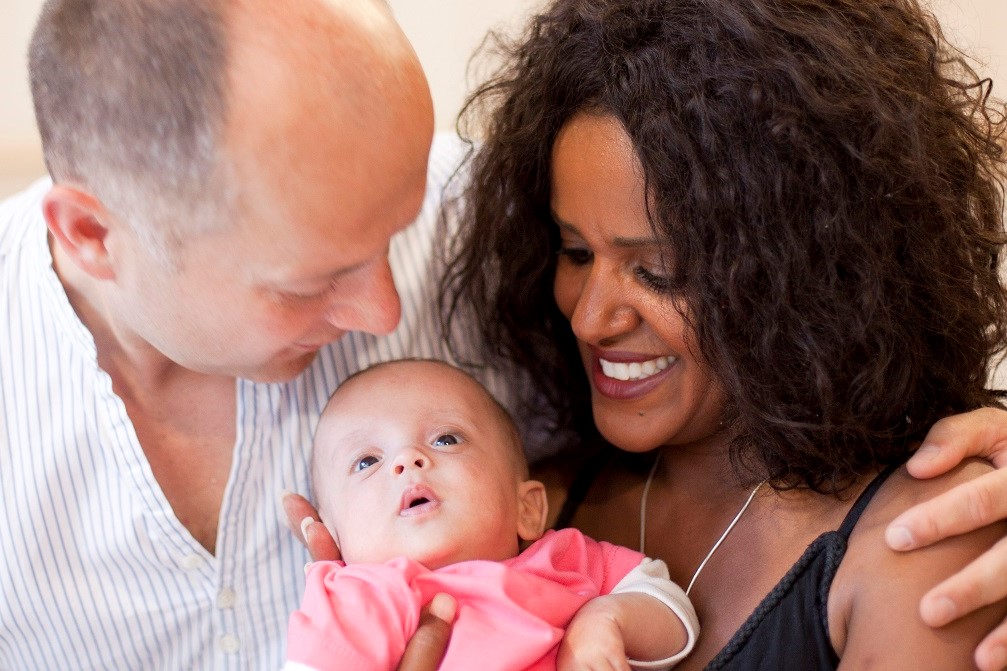
Infant- and family-centred developmental care
Developmental support consists of a variety of intervention strategies in addition to medical care, to protect and promote the growth and development of a baby. Developmental care includes among others the control of external stimuli, specific supportive behavioural techniques such as the positioning of the baby, skin-to-skin care, or the integration of parents in care activities and in the decision-making regarding the baby’s treatment and care. Developmentally supportive care creates a neonatal unit environment that minimises stress for the baby, the parents and healthcare professionals. It reduces pain and provides a developmentally appropriate sensory experience for the individual baby. Studies suggest that babies who receive developmentally supportive care may stay in hospital for less time and gain weight better.